Ocular Sarcoidosis_ Everything to Know
Ocular Sarcoidosis: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Ocular Sarcoidosis
Ocular sarcoidosis is a condition where granulomas, or small clusters of tissue, form in different parts of the body, including the eyes. These granulomas can cause inflammation and damage to organs, and when they affect the eyes, the condition is known as ocular sarcoidosis. One of the most severe manifestations of ocular sarcoidosis is uveitis, which causes eye pain, redness, and potential vision loss. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing the condition effectively.
What is Ocular Sarcoidosis?
Ocular sarcoidosis refers to the inflammation of the eyes caused by sarcoidosis, a disease that leads to the formation of granulomas in various body parts. It commonly affects adults between the ages of 20 and 40. Sarcoidosis can involve several organs, with the lungs being the most frequently impacted. However, the disease can also affect the eyes, causing symptoms such as eye redness, pain, and blurred vision. Uveitis, the inflammation of the uvea, is one of the main eye complications resulting from ocular sarcoidosis.
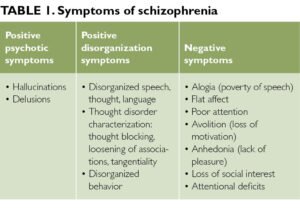
Symptoms of Ocular Sarcoidosis
Ocular sarcoidosis can present with a variety of symptoms, depending on the area of the eye affected. Common signs include:
-
Dry eyes
-
Itchy or burning eyes
-
Redness and occasional pain
-
Blurry vision
-
Sensitivity to light
-
Black spots or floaters in vision
-
Decreased color vision
It is also possible for individuals with sarcoidosis to develop small, yellowish bumps on their eyes. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice.
Causes and Mechanism of Ocular Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that can affect multiple organs, but it most frequently targets the lungs. The condition typically develops in adults between the ages of 20 and 40. When sarcoidosis affects the eyes, it may lead to uveitis, an inflammation of the uvea, which is the middle layer of the eye. Uveitis occurs when white blood cells accumulate in the eye, causing the tissues to become sticky, leading to adhesions between internal structures such as the iris and lens. This can increase eye pressure and lead to pain, redness, and light sensitivity. If left untreated, it can even result in blindness.
How is Ocular Sarcoidosis Diagnosed?
To diagnose ocular sarcoidosis, an ophthalmologist will perform a thorough eye examination. This includes using a slit-lamp microscope to examine the front portion of the eye and dilating the pupils with special drops to assess the back of the eye. The doctor will look for signs of inflammation and other abnormalities. Because dry eyes are common in sarcoidosis, a Schirmer test may be conducted to evaluate tear production by placing blotting paper in the lower eyelid.
Treatment Options for Ocular Sarcoidosis
The treatment for ocular sarcoidosis depends on which part of the eye is affected. Your ophthalmologist may recommend the following:
-
Anti-inflammatory eye drops to reduce inflammation
-
Dilating drops to prevent the iris from sticking to the lens
-
Artificial tears to address dryness caused by lacrimal gland dysfunction
-
Corticosteroids, either orally or in other forms, for more persistent cases
With appropriate treatment, the progression of the disease can be slowed, and potential long-term damage to the eyes can be prevented.
Coping with Ocular Sarcoidosis
Regular eye exams are essential for managing ocular sarcoidosis, as eye complications are common with this condition. Early detection and treatment can prevent permanent damage to the eyes. Patients with sarcoidosis should consider annual eye exams with an ophthalmologist, especially during the first few years after diagnosis.
Key Takeaways
Ocular sarcoidosis is a serious condition that requires early diagnosis and management to prevent vision loss. Symptoms like eye redness, pain, and blurry vision should not be ignored. While the disease primarily affects the lungs, it can also cause significant issues in the eyes. Regular monitoring and prompt treatment can help control symptoms and prevent long-term damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Sarcoidosis Cause Blindness?
Yes, ocular sarcoidosis can lead to serious vision problems, including blindness. The inflammation in the eye can increase intraocular pressure and contribute to glaucoma, potentially resulting in partial or total blindness if not treated effectively.
How is Ocular Sarcoidosis Tested?
To test for ocular sarcoidosis, healthcare providers use a combination of a detailed medical history, physical examination, and tests such as a tissue biopsy and slit-lamp examination to confirm the presence of uveitis or other eye-related issues.
What are the Symptoms of Ocular Sarcoidosis?
Common symptoms include eye redness, pain, light sensitivity, blurred vision, and the appearance of floaters. If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to consult an ophthalmologist for a full evaluation.
By improving awareness and providing effective treatment options, individuals with ocular sarcoidosis can better manage the condition and protect their vision.